Expansion
of steppe pastoralists (Narasimhan et al. 2019)
How
much of the present-day European gene pool comes from the indigenous
hunter-gatherers? How much from Neolithic farmers of Anatolian origin? And how
much from steppe pastoralists of the Don-Volga area? There is no easy answer.
A
“founder event” results when a few people split off from their original
population and found a new one. The fewer they are, the likelier they will
differ genetically, on average, from the original population. The founder event
is a “bottleneck” through which only a small fraction of the original genetic
diversity can pass into the new population.
A
founder event is one of three reasons why adjacent populations may differ from
each other genetically. The other two are:
Natural selection – The boundary
between two adjacent populations often corresponds to a change in the natural
environment (vegetation, climate, etc.) or the cultural environment (diet, way
of life, rules and prohibitions, sexual division of labor, etc.). The two
populations are thus subjected to different regimes of natural selection.
Population
admixture or replacement – One of the two adjacent populations has admixed
with or been replaced by a population that has moved into the area.
In
practice, a founder event overlaps with differences in natural selection. When
pioneers move into a new area, they tend to be better suited to the local
conditions than the people they left behind. The less suited are less likely to
go, and if they do go they are more likely to go back … or die. So, from the
outset, there already is some selection.
A
new study of ancient DNA has shown that founder effects have been more frequent
and more “extreme” than previously thought: “In humans, we find that over half
of the analyzed populations have evidence for recent founder events, associated
with geographic isolation, modes of sustenance, or cultural practices such as
endogamy” (Tournebize et al. 2022, p. 1)
Contrary
to popular belief, Ashkenazi Jews are not the outcome of a particularly extreme
founder event:
Across worldwide populations, we
identified 53 groups that have experienced more extreme founder events (with
significantly higher founder intensity) than AJs [Ashkenazi Jews], who have
high rates of recessive diseases due to their history of founder events
(Tournebize et al. 2022, p. 7)
Perhaps
those recessive diseases are not due to a founder event. Perhaps they are a
side-effect of selection for an adaptive trait. If a founder effect had been the
cause, those diseases would be distributed randomly over different metabolic
pathways. Actually, they are all associated with excessive storage of
sphingolipids, a key component of neural tissue (Cochran et al. 2006; Diamond
1994).
Founder
events seem to have been frequent among ancestral Europeans, regardless of
whether they were hunter-gatherers, farmers, or pastoralists. But those events
seem to have been more “intense” among European hunter-gatherers. In other
words, founder groups were smaller and spent more time passing through the
population bottleneck.
Recent analysis has shown that present-day
Europeans are a mixture of three major ancestry groups related to ancient
European hunter-gatherers, Anatolian farmers, and Eurasian Steppe pastoralists.
[…] Across the three groups, we found that the frequency of founder events was
similar, ranging between 90–100%. However, the average founder intensity was
significantly higher in European hunter-gatherers […] compared to the Near
Eastern farmers […] or the Steppe pastoralists. (Tournebize et al. 2022, p. 11)
Hunter-gatherers
had more intense founder events because they had a lower population density.
Founder groups were thus smaller and less representative of the original
population from which they came.
… we found local hunter-gatherer groups
had more extreme founder events than the Neolithic farmers or Bronze Age
individuals. This suggests that population sizes in Europe have increased over
time, coupled with changes in ancestry and transitions in lifestyle. Our
results are consistent with a recent study that measured short runs of
homozygosity in ancient Europeans and found a similar increase in population
size during the Neolithic period. Our results are also in agreement with
archeological evidence for increased population size during the Neolithic
transition. (Tournebize et al. 2022, p. 14)
This
takes us back to the previous quote: Europeans are a mix of indigenous
hunter-gatherers, Anatolian farmers, and steppe pastoralists. These three groups,
and their roles in European prehistory, can be summarized as follows:
·
Farmers
began to move into Europe from present-day Turkey about 10,000 years ago.
Initially, they advanced rapidly through territory inhabited by small nomadic
bands.
·
About
7,000 years ago, the wave of advance stalled along a line running from the Low
Countries to the Black Sea. To the north, along the North Sea and the Baltic,
were large semi-sedentary communities of hunter-fisher-gatherers who could less
easily be replaced because they were so numerous.
·
About
a thousand years later, farming resumed its northward advance, although the
advance was now much more a matter of people adopting farming rather than being
replaced by farmers.
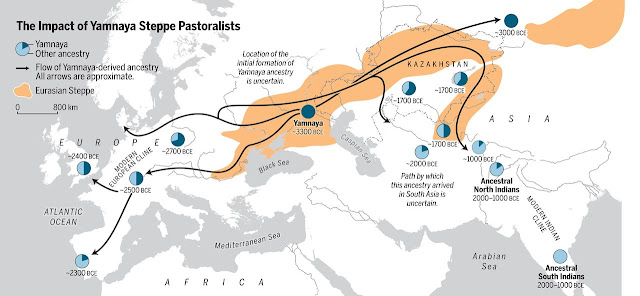
·
Meanwhile,
around 5,400 years ago, some hunter-gatherers in the Don-Volga area adopted
pastoralism and began to expand westward into Europe and southeastward into the
Middle East, Central Asia, and South Asia. They may have been ancestral
Indo-Europeans.
How
much did each of the three groups contribute to the European gene pool? Which
group contributed the most and which the least? The question is hard to answer,
for three reasons:
Double counting
The
hunter-gatherers of Mesolithic Europe contributed to the present European gene
pool both directly and indirectly. The steppe pastoralists were themselves
indigenous hunter-gatherers who had adopted pastoralism, plus an admixture of
up to 18% from Anatolian farmers. As the Anatolian farmers pushed into Europe,
they became gradually “Europeanized” through intermixture with local
hunter-gatherers. It is also possible that the Anatolian farmers were
themselves the product of an earlier expansion of European hunter-gatherers
into the Middle East (Frost 2014).
Founder events
We
measure population replacement by measuring the degree of genetic difference
between the original group and the one that replaced it. Is that a valid method?
Let’s take the replacement of hunter-gatherers by farmers, and let’s assume that
all of the farmers were descended from hunter-gatherers who had adopted
farming. The two groups would still be genetically different. The farmers would
have been the product of a founder event—a small and genetically
unrepresentative group of hunter-gatherers who had decided to take up farming.
Differences in
natural selection
Population
replacement is hard to measure for another reason: hunter-gatherers and farmers
lived under different regimes of natural selection. They were selected for
their ability to adapt to different diets, types of shelter, and means of
subsistence. To go from one way of life to the other required not only cultural
change but also genetic change.
For
instance, the population frequency of haplogroup U shows a sharp break at the
time boundary between late hunter-gatherers and early farmers (Bramanti et al.
2009). That break strongly suggests that the original Europeans were largely
replaced by farmers spreading into Europe from the Middle East. Yet haplogroup
U would persist in Denmark at high frequencies long after the transition to
farming (Melchior et al. 2010). In Latvia and Ukraine it would persist into
Neolithic times (Jones et al. 2017). Haplogroup U probably disappeared from the
European gene pool because it ceased to be adaptive. It has been shown to shift
the energy balance away from ATP synthesis and toward production of body heat,
a useful adaptation if you sleep in makeshift shelters and pursue game in all
kinds of weather (Balloux et al. 2009; Montiel-Sosa et al. 2006). It’s less
useful if you sleep in a warmer environment and can plan your outdoor
activities.
Conclusion
Whenever
I make this argument, the counter-argument is that founder events and natural
selection could not possibly explain all of the genetic difference we see
between late hunter-gatherers and early farmers in Europe. I agree. I’m just
saying that the magnitude of the demographic replacement has been overestimated.
References
Balloux
F., L.J. Handley, T. Jombart, H. Liu, and A. Manica. (2009). Climate shaped the
worldwide distribution of human mitochondrial DNA sequence variation. Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
Biological Sciences 276: 3447-3455.
https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2009.0752
Bramanti,
B., M.G. Thomas, W. Haak, M. Unterlaender, P. Jores, K. Tambets, I.
Antanaitis-Jacobs, M.N. Haidle, R. Jankauskas, C.J. Kind, et al. (2009).
Genetic discontinuity between local hunter-gatherers and Central Europe's first
farmers. Science 326: 137-140. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1176869
Cochran,
G., J. Hardy, and H. Harpending. (2006). Natural history of Ashkenazi
intelligence. Journal of Biosocial
Science 38(5): 659-693. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021932005027069
Diamond,
J.M. (1994). Jewish Lysosomes. Nature 368:
291-292. https://doi.org/10.1038/368291a0
Frost,
P. (2014). The new European phenotype: expansion into the Middle East. Evo and Proud, January 25. https://evoandproud.blogspot.com/2014/01/the-new-european-phenotype-expansion.html
Jones,
E.R., G. Zarina, V. Moiseyev, E. Lightfoot, P.R. Nigst, A. Manica, et al.
(2017). The Neolithic transition in the Baltic was not driven by admixture with
early European farmers, Current Biology
27(4): 576-582.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.12.060
Melchior,
L., N. Lynnerup, H.R. Siegismund, T. Kivisild, and J. Dissing. (2010). Genetic
diversity among ancient Nordic populations. PLoS
One 5(7): e11898
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011898
Montiel-Sosa, F., E.
Ruiz-Pesini, J.A. Enriquez, A. Marcuello, C. Diez-Sanchez, J. Montoya, D.J.
Wallace, and M.J. López-Pérez, (2006). Differences of sperm motility in
mitochondrial DNA haplogroup U sublineages. Gene
368: 21-27.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2005.09.015
Narasimhan,
V.M., N. Patterson, P. Moorjani, N. Rohland, R. Bernardos, S. Mallick, I.
Lazaridis, et al. (2019). The formation of human populations in South and
Central Asia. Science 6: 365(6457):
eaat7487. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat7487
Tournebize,
R., G. Chu, and P. Moorjani. (2022). Reconstructing the history of founder
events using genome-wide patterns of allele sharing across individuals. PLoS Genet 18(6): e1010243. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1010243
Did the steppe pastoralists introduce lactase tolerance into the modern European population?
ReplyDeleteHi Luke,
ReplyDeleteApparently not.
"The absence of LP [lactase persistence] before the late Neolithic and the correlation between its appearance and migration from the steppes has therefore led to the alternative hypothesis of LP first arising in a pastoralist steppe population and then being brought to western Europe at the beginning of the Corded Ware culture (2). However, these steppe populations have been estimated to display a very small amount of LP (−13.910:T frequency of 0% and approximately 6% in two studies from the Bronze Age)(2, 85), challenging the idea that they are the source populations for LP."
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28426286/